
An effective concentration of 1 mol/L for each aqueous species or a species in mercury amalgam (an alloy of mercury. Electron charge, (symbol e), fundamental physical constant expressing the naturally occurring unit of electric charge, equal to 1.602176634 × 1019 coulomb. That is, at short-enough distances, quantum fluctuations within the vacuum of space surrounding an electron begin to have calculable effects that have measurable consequences in atomic and particle physics.īased on the assumption of a simple mechanical model, attempts to model the electron as a non-point particle have been described by some as ill-conceived and counter-pedagogic. The data values of standard electrode potentials ( E ) are given in the table below, in volts relative to the standard hydrogen electrode, and are for the following conditions: A temperature of 298.15 K (25.00 C 77.00 F). A moving charge also produces a magnetic field. Electric charges produce electric fields. Electrons have an electric charge of (-1), which is equal but opposite to the charge of a proton, which is (+1). Note that because we investigate electron charge distribution function by considering the equation of motion of its segment of charge with self-interaction. What is the definition of an electron Richard Laming. The proton has a charge of +e, and the electron has a charge of e. Instead, it is determined by the coulomb, which is the standard unit of quantity of electrical charge (C).

R e = 1 4 π ε 0 e 2 m e c 2 = 2.8179403227 ( 19 ) × 10 − 15 m = 2.8179403227 ( 19 ) fm, is roughly the length scale at which renormalization becomes important in quantum electrodynamics. In the Standard Model, charge is an absolutely conserved quantum number. Calculate the mass of a proton if the charge to mass ratio of an electron is 1.758820×1011 C kg1 and it is known that the.

The classical electron radius is given as Calculate the ratio between the wavelength of an electron and a proton, if the proton is moving at half the velocity of the electron (mass of the proton 1.67×1027kg mass of the electron 9.11×1028g ). Nevertheless, it is useful to define a length that characterizes electron interactions in atomic-scale problems. The currently accepted value for e/m is 1.758820. The relationship between the voltage (V), resistance (R), and current (I) is VIR this is known as Ohms law.
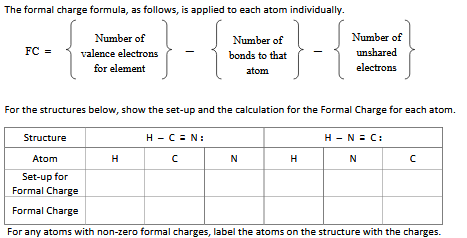
According to modern understanding, the electron is a point particle with a point charge and no spatial extent. In this experiment you will measure e/m, the ratio of the charge of an electron to the mass of an electron. It links the classical electrostatic self-interaction energy of a homogeneous charge distribution to the electron's relativistic mass-energy. The classical electron radius is a combination of fundamental physical quantities that define a length scale for problems involving an electron interacting with electromagnetic radiation.
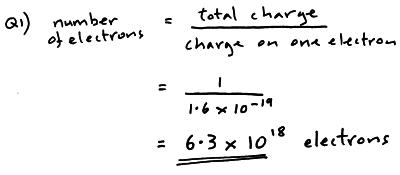
In the SI system of units, the value of the elementary charge is exactly defined as e īy combining the best measured value of the antiproton charge (below) with the low limit placed on antihydrogen's net charge by the ALPHA Collaboration at CERN.Physical constant providing length scale to interatomic interactions 4 years ago Sir, How Did we find the charge of electrons or protons in Coulombs C ( 4 votes) Upvote Flag Rajashree 3 years ago 1e/1.610-19-1.610-19/1.610-19c6. The elementary charge, usually denoted by e, is a fundamental physical constant, defined as the electric charge carried by a single proton or, equivalently, the magnitude of the negative electric charge carried by a single electron, which has charge −1 e. The elementary charge, usually denoted by e, is a fundamental physical constant, defined as the electric charge carried by a single proton or, equivalently. Each electron carries the same quantity of charge, which is the negative of the elementary charge e. Charge carried by one proton or electron Elementary charge Current in metal wires is usually carried by electrons.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
